Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Ali, Y.*; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
Dai-34-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/12
A new communication avoiding (CA) Krylov solver with a FP16 (half precision) preconditioner is developed for a semi-implicit finite difference solver in the Gyrokinetic Toroidal 5D full-f Eulerian code GT5D. In the solver, the bottleneck of global collective communication is resolved using a CA-Krylov subspace method, and halo data communication is reduced by the FP16 preconditioner, which improves the convergence property. The FP16 preconditioner is designed based on the physics properties of the operator and is implemented using the new support for FP16 SIMD operations on A64FX. The solver is ported also on GPUs, and the performance of ITER size simulations with 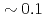 trillion grids is measured on Fugaku (A64FX) and Summit (V100). The new solver accelerates GT5D by
trillion grids is measured on Fugaku (A64FX) and Summit (V100). The new solver accelerates GT5D by 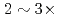 from the conventional non-CA solver, and excellent strong scaling is obtained up to 5,760 CPUs/GPUs both on Fugaku and Summit.
from the conventional non-CA solver, and excellent strong scaling is obtained up to 5,760 CPUs/GPUs both on Fugaku and Summit.
Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Shimyureshon, 22(2), p.89 - 97, 2003/06
This is a collection of review article related to the "Multiple Time and Spatial Scale Plasma Simulation" of various fields including fundamental research area of self-organization, magnetic and laser fusion field, space and astrophysics field where a plasma plays an essential roles.
Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
In this talk, main results from the 3rd cycle IFERC-CSC project GT5DISO are reviewed. Full-f gyrokinetic simulations of ion temperature gradient driven turbulence are performed for hydrogen and deuterium plasmas with various normalized machine size and heating power, and hydrogen isotope effects on the confinement property of fusion plasmas. An experimental confinement scaling is recovered with respect to a hydrogen isotope effect through the normalized machine size, while an influence from the ion mass is not clear. This result suggests that simulations including electron turbulence are needed to fully explain the hydrogen isotope effects.
Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
Decaying turbulence simulations of ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence with adiabatic electrons and ion temperature gradient driven trapped electron mode (ITG-TEM) turbulence with kinetic electrons are performed using a full-f gyrokinetic code. Nonlinear critical temperature gradients exceeding linear critical temperature gradients are observed in both simulations, and mechanisms to sustain them are investigated. It is found that unlike zonal flows in the ITG turbulence, the ITG-TEM turbulence produces corrugated electron density profiles, which form radial electric fields with strong shear following a force balance relation.
Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
A communication-avoiding generalized minimal residual (CA-GMRES) method is applied to the gyrokinetic toroidal five dimensional Eulerian code GT5D, and its performance is compared against the original code with a generalized conjugate residual (GCR) method on the Oakforest-PACS (KNL). The CA-GMRES method has less memory access and collective communications than the GCR method, and thus, is suitable for future Exa-scale architectures with limited memory and network bandwidths. It is shown that compared with the original GCR version, the CA-GMRES version is accelerated by 1.32x, and the cost of data reduction communication is reduced from ~13% to ~1% of the total cost at 1,280 nodes.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu; Matsumoto, Kazuya*; Asahi, Yuichi*; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
no journal, ,
We propose a modified communication-avoiding generalized minimal residual (CA-GMRES) method, which reduces both computation and memory access by 30% with keeping the same CA property as the original CA-GMRES method. These numerical properties, less communication and computation with higher arithmetic intensity, are promising features for future exascale machines with limited memory and network bandwidths. The modified CA-GMRES method is applied to a large scale non-symmetric matrix in an implicit solver of the gyrokinetic toroidal five dimensional Eulerian code GT5D, and its performance is estimated on the Oakforest-PACS (KNL). The numerical experiment shows that compared with the generalized conjugate residual method, computing kernels are accelerated by 1.5x, and the cost of data reduction communication is reduced from 12.5% to 1% of the total cost at 1,280 nodes.